Back to School: 10 Ways to Improve Israel’s Education System
How to help students prepare for the future job market? Ten experts offer unique ideas on how to make education in Israel more innovative and creative
Below are interviews with 10 experts sharing their unique ideas on how to make education in Israel more innovative and creative.
Yaron Neudorfer, founder and CEO of Social Finance Israel: Invest in social impact bonds
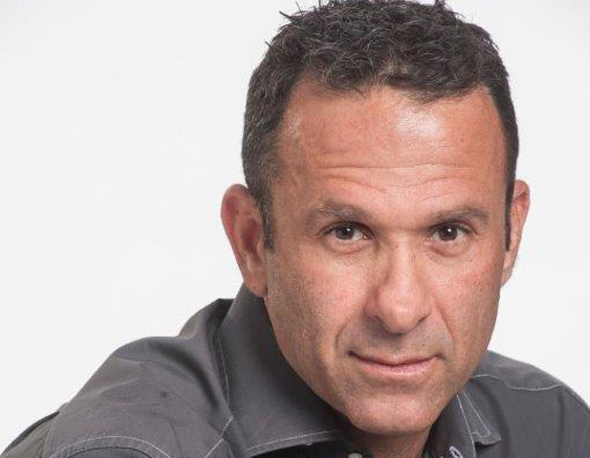 Yaron Neudorfer, founder and CEO of Social Finance Israel/ Photo: Ilya Malinkov
Yaron Neudorfer, founder and CEO of Social Finance Israel/ Photo: Ilya Malinkov Established in 2013, SFI is a social enterprise working to promote socially-minded investment through innovative financing tools. The idea of SIB is simple: investment firms raise funds for social causes and get paid by private organizations or the government based on accomplishments. A new project launched by SFI this year is designed to raise the number of Bedouin students in the southern town of Rahat who get a high school diploma. SFI has already raised NIS 15 million (approximately $4.2 million) for the project, which will see the Israeli Ministry of Education pay based on the numbers of graduating students, Neudorfer told Calcalist in a recent interview.
According to Neudorfer, SIBs could also help retain teachers, many of whom leave the profession after just a few years on the job due to difficult financial conditions.
Rinat Rosenberg-Kima, the Faculty of Education in Science and Technology, Technion Israel Institute of Technology: Social robots will assist teachers
 Rinat Rosenberg-Kima. Photo: Noam Tor
Rinat Rosenberg-Kima. Photo: Noam Tor In an experiment Rosenberg-Kima conducted at Tel Aviv University, she tested the use of a robot assistant during group work sessions. Rosenberg-Kima found that students are sometimes more comfortable approaching a robot, which is not critical or judgemental and has more patience than most human teachers. Robots could be a solution for what is considered menial tasks in teaching, such as teaching the multiplication table, Rosenberg-Kima said. Still, it will take time for robots to comprehend the complicated social interactions in the classroom. According to Rosenberg-Kima, teaching is a much more complex task than driving autonomously.
Miriam Leibowitz-Assaraf: a secular girls-only school
 Miriam Leibowitz-Assaraf. Photo:Karen Mazor
Miriam Leibowitz-Assaraf. Photo:Karen Mazor This school year will see the launch of a new secular girls-only education program (Jewish religious education in Israel is often segregated). Dubbed Inbar, the program is offered for grades 7 through 12 and is designed to provide girls with an equal opportunity for academic excellence.
Miriam Leibowitz-Assaraf, who heads the program, believes that separate education can help girls level the academic playing field. Studies show that educational staff often possesses gender bias, Leibowitz-Assaraf told Calcalist in a recent interview. According to her, graduates of female-only programs go on to be more socially and politically active. The new program will emphasize science, technology, and engineering studies. Girls will study robotics and meet with female role models.
Inbal Chameides, co-founder and managing director at P.I.E Challenge: Teach mindfulness at school
 Inbal Chameides. Photo: Eyal Marilus
Inbal Chameides. Photo: Eyal Marilus Danel Ben Namer, Revah Naki: teach finance to schoolchildren
 Daniel Ben Namer. Photo: Omer Avraham
Daniel Ben Namer. Photo: Omer Avraham According to Danel Ben Namer, financial education should be a required course in school. Ben Namer heads Revah Naki, a social project set to promote early financial education. According to him, kids need to learn how to be smart consumers, how to manage a household budget, how to deal with banks and credit card companies, and what to look out for when taking a loan.
“Financial education helps understand the meaning of debt, when to take a loan and when to pass on it,” Ben Namer told Calcalist, adding that the number one factor dissuading adults from dealing with their finances is financial illiteracy.
According to Ben Namer, 20% of Israeli schools offer some financial education classes, but these programs are few and not comprehensive. He believes every high school student should get four weekly hours of financial training.
Shay Tzur, a researcher at the Bank of Israel: programming as a mandatory course
 Shay Tzur. Photo: Bank of Israel
Shay Tzur. Photo: Bank of Israel According to the 2018 OECD Teaching and Learning International Survey (TALIS), 40% of Israeli principles stated they have a shortage of digital teaching aids, compared with an OECD average of 25%.
The use of computers in schools needs to become much broader and programming should be a mandatory class, not just for those majoring in computer sciences, Tzur said in an interview.
More digital teaching aids could help with the country’s shortage of quality educational staff, Tzur added. “If teachers could let some of the stronger pupils study independently on a computer, they could have more time to assist other students.”
Shirly Avargil, the Faculty of Education in Science and Technology at Technion Israel Institute of Technology: escape rooms as skill tests
 Shirly Avargil. Photo: Nitzan Zohar, Technion
Shirly Avargil. Photo: Nitzan Zohar, Technion As part of an experiment, Avargil intends to construct an escape room meant to evaluate students in areas that are usually hard to grade—teamwork, creative thinking, and problem solving.
“Escape rooms utilize many skills that are necessary in the 21st century and can act as an alternative to tests,” Avargil said in an interview.
Yoel Rothschild, Deputy Director General and Head of the Research, Development, and Training Administration at non-state funded school and college chain ORT Israel: strengths-oriented study
 Yoel Rothschild. Photo: Orel Cohen
Yoel Rothschild. Photo: Orel Cohen
Rothschild believes the educational system tends to put too much emphasis on a student’s weaknesses instead of focusing on their strengths. In its schools, ORT attempts to map out students strengths, as individuals, as a class, and as a school.
ORT uses this analysis to group students with similar strengths and weaknesses, using the subjects they are better at to help students overcome difficulties in other subjects. “There are quite a few students that have problems in a regular class but are very good at sports,” Rothschild said in an interview. “I can have them research athletes from around the world to help them learn English or teach them sports-related physics, math, and biology.” When it comes to art, talking about colors is basically teaching science and technology, he added.
Hagit Elias, CEO of Momentum The Growth Engine of Automotive Professions Ltd.: car technicians for the digital age
 Hagit Elias. Photo: Orel Cohen
Hagit Elias. Photo: Orel Cohen Vocational-technical schools fail to train students for work with new technologies and to take into account promotion and advancement opportunities, which were not available in the past, Elias said in a recent interview.
Momentum offers high schoolers autonomous vehicle and artificial intelligence courses, complete with advanced math and computer science studies. The program operated as a pilot in two schools last year and will run at six schools this year.
Students are encouraged to pursue careers from car technician to engineer and the program is not meant to send every one of them to work at a car shop, Elias said.
Ronnie Lidor, president of the Wingate Institute, Israel's National Centre for Physical Education and Sport: daily PE classes
 Ronnie Lidor. Photo: Amit Sha'al
Ronnie Lidor. Photo: Amit Sha'al Currently, Israeli pupils only take two weekly physical education classes, but Lidor believes this number should go up to six classes a week, or one academic hour a day, even at the price of forgoing other subjects. “A large portion of the population is not physically active and in order to change this you have to start off at an early age,” Lidor said in a recent interview with Calcalist.
In addition to physical exercise, these classes should include theoretical knowledge on nutrition, personal hygiene, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, Lidor said. Physical exercise can help save on future medical treatments and also improves concentration and decision making, he said.



