Revium Rx’s Nanoparticle Technology Aims to Tackle Antibiotic Resistance and Beyond
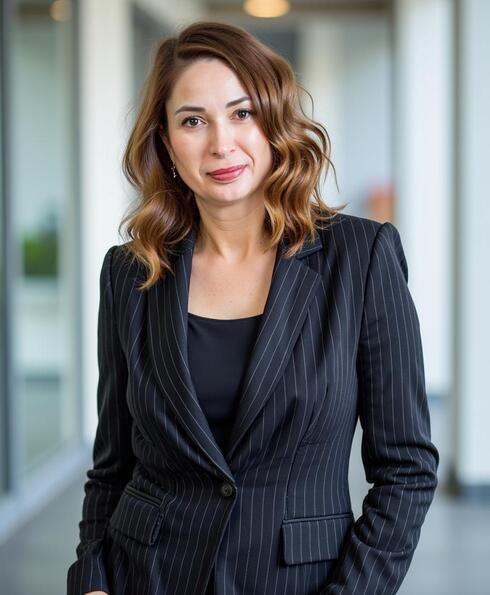
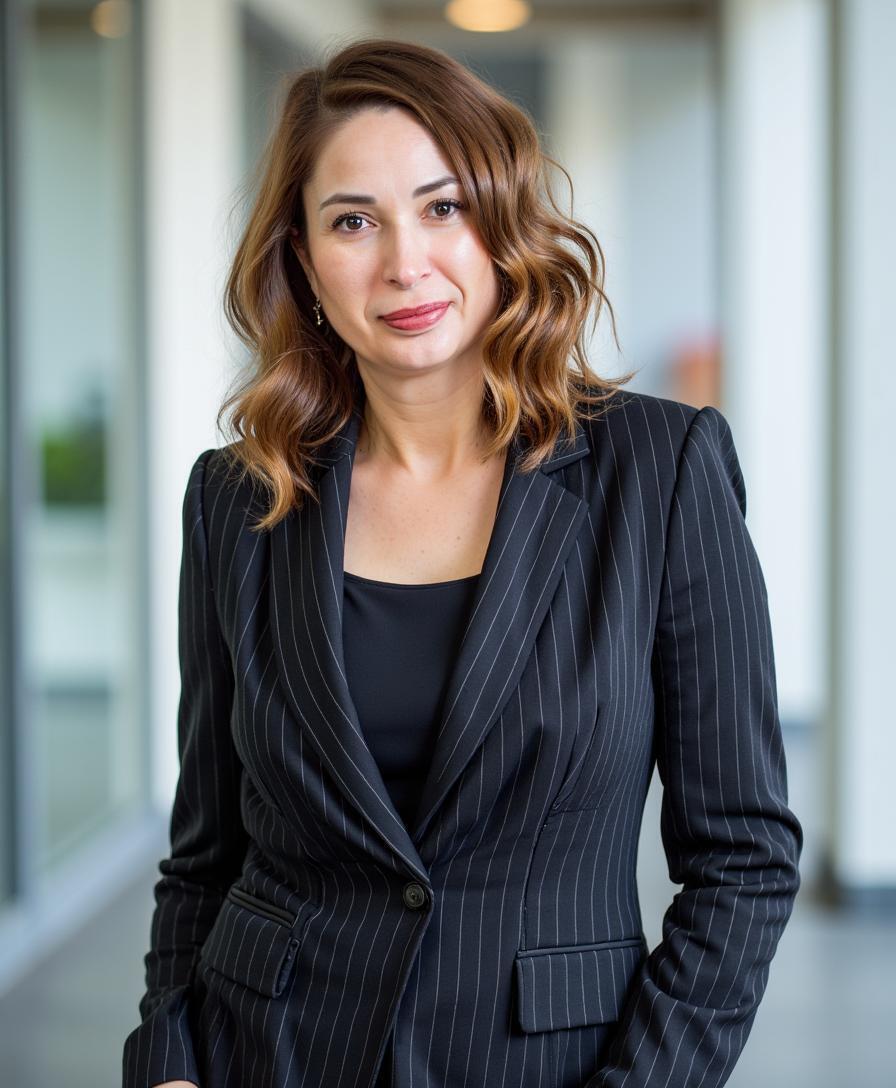
"Without new treatment approaches, we risk returning to a time when even minor infections could be life-threatening", says Inna Martin, COO and President
In recent weeks, reports of antibiotic-resistant bacteria spreading in Israeli hospitals have raised concerns among healthcare professionals and the general public. The phenomenon, which has been growing worldwide, poses a serious threat to modern medicine, as infections once considered treatable are becoming increasingly difficult to manage. While the challenge is significant, scientific innovation is providing new potential solutions. One of the companies working to address this issue is Revium Rx, an Israeli biotech firm developing nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems.
Israel's healthcare system continues to excel while addressing one of the most pressing global health challenges: antimicrobial resistance (AMR). In Israel, as elsewhere, hospital-acquired infections and AMR pathogens have risen, especially since the pandemic, with a 20-30% increase across healthcare settings. Such infections elevate mortality rates and strain the health system. In 2019, Israel reported approximately 903 deaths directly attributable to antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and around 3,800 deaths associated with AMR.
In response to these growing concerns, a US-based pharmaceutical start up Revium Rx recently announced the acquisition of LipoVation Ltd., an Israeli development-stage company specializing in lipid-based nanoparticle medicines. LipoVation was conceptualized by world-renowned scientist Prof. Yechezkel Barenholz, the inventor of Doxil, the first FDA-approved nano-medicine drug. This strategic move positions Revium Rx at the forefront of nanoparticle-based therapeutics and expands its pipeline in infectious diseases.
As part of this transition, Inna Martin has been appointed President and COO, where she will lead the company's development efforts, focusing on preparations for clinical trials of Nano-Mupirocin, is a new, potent lipid-based formulation of a highly effective antibiotic that was previously limited to topical use only.
The Global Challenge of Antibiotic Resistance
Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria change in a way that makes antibiotics less effective or completely ineffective against them. This makes infections significantly harder to treat and increases the risk of disease spread, severe illness, disability, and death. The overuse and misuse of antibiotics in humans, animals, and agriculture have accelerated this problem, and factors such as poverty and inequality exacerbate the crisis by limiting access to proper medical care.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), antibiotic resistance was directly responsible for 1.27 million deaths globally in 2019, and it contributed to 4.95 million deaths overall. During the COVID-19 pandemic, with increased complications, overuse of antibiotics, and strain on healthcare systems, these numbers are believed to have grown significantly, although comprehensive post-pandemic data is still emerging. The economic burden is also substantial, leading to longer hospital stays, higher medical costs, and increased mortality rates. As noted, Israel has also experienced a 20–30% increase in hospital-acquired infections and AMR pathogens, especially since the COVID-19 pandemic. This underscores the escalating challenge of AMR in Israel, highlighting the need for ongoing surveillance and intervention strategies. Israel’s health system monitors and publishes reports on resistant pathogens in order to assess progress and ensure transparency. Continuous monitoring of multiple indicators allows them to respond rapidly to outbreaks and emerging threats.
"Antibiotic resistance is not a theoretical problem—it’s a growing global and local health crisis," explains Martin. "Without new treatment approaches, we risk returning to a pre-penicillin era when even minor infections could be life-threatening." Israel has developed a robust national strategy, led by the National Center for Infection Prevention and Antibiotic Resistance, that focuses on three critical areas: reducing hospital-acquired infections, training specialists, and continuous monitoring. Despite these efforts, challenges remain, including the rise in infections and the need for more specialists.
Addressing Antibiotic Resistance with Targeted Drug Delivery
The market potential for new antibiotics targeting resistant bacteria such as Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) , Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE) , and drug-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae is substantial, given the rising prevalence of these infections and the urgent need for effective treatments.
MRSA and VRE Antibiotic Market:
In 2023, the global market for antibiotics targeting VRE and MRSA was valued at approximately USD 4.4 billion. DataHorizon Research
Projections indicate that this market will reach around USD 6.26 billion by 2032 , reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 4% during the forecast period.
One of Revium Rx’s most advanced developments is Nano-Mupirocin, a liposomal formulation of mupirocin, an antibiotic known for its ability to combat bacteria resistant to other treatments. Traditionally, mupirocin has been limited to topical use because it is rapidly broken down in the bloodstream, preventing systemic administration.
Revium Rx has developed a nanoparticle-based formulation that enables systemic delivery, allowing the drug to circulate for longer periods and effectively target multi-drug-resistant bacteria such as MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) and VRE (Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium). "With Nano-Mupirocin, we aim to provide a much-needed alternative for severe bacterial infections where traditional antibiotics are no longer effective," says Martin. Israel is actively working to reduce hospital-acquired infections by implementing stringent protocols, particularly in intensive care units and long-term care facilities. These efforts have led to a 70% reduction in some hospital-acquired infections. Furthermore, in 2025, Israel aims to recruit and train 60 new infection prevention physicians to enhance AMR response.
Preclinical studies of Nano-Mupirocin have shown promising results, demonstrating enhanced efficacy, extended bioavailability, and targeted bacterial eradication compared to conventional treatments. The company is currently preparing for Phase I clinical trials, expected to begin in early 2026.