Fiverr CEO: "GenAI will create more jobs than it will eliminate"
Micha Kaufman was speaking on a panel with Dana Maor, senior partner at McKinsey & Company, and Barak Regev, Country Director of Google Israel
In an era dominated by artificial intelligence (AI), the intersection of human capital and technological advancement takes center stage. The third day of Google and Calcalist’s Startup Week delved into this critical nexus, led by a panel of industry experts. Addressing the profound shifts reshaping the labor market, they explored the emergence of new roles amidst the disappearance of traditional ones. From McKinsey's insights into AI's transformative potential to Fiverr's perspective on the freelancer landscape, the discussion illuminated the challenges and opportunities inherent in this AI-driven paradigm. As organizations grapple with adaptation, the imperative to harness human potential alongside technological innovation becomes increasingly apparent.
"If a few months ago clients questioned the reality and necessity of addressing AI, today's inquiries have shifted to how organizations should prepare and manage their human capital," says Dana Maor, senior partner at McKinsey & Company. "We observe that generative AI significantly accelerates AI's application, bringing automation to roles previously untouched. We anticipate that within a decade, 60% of customer interactions will involve AI, and software developers could see a 55% productivity improvement through AI utilization. Additionally, tasks such as writing job descriptions and conducting employee interviews in the human resources department could be automated. This is a profound change that many are still grasping."
1 View gallery
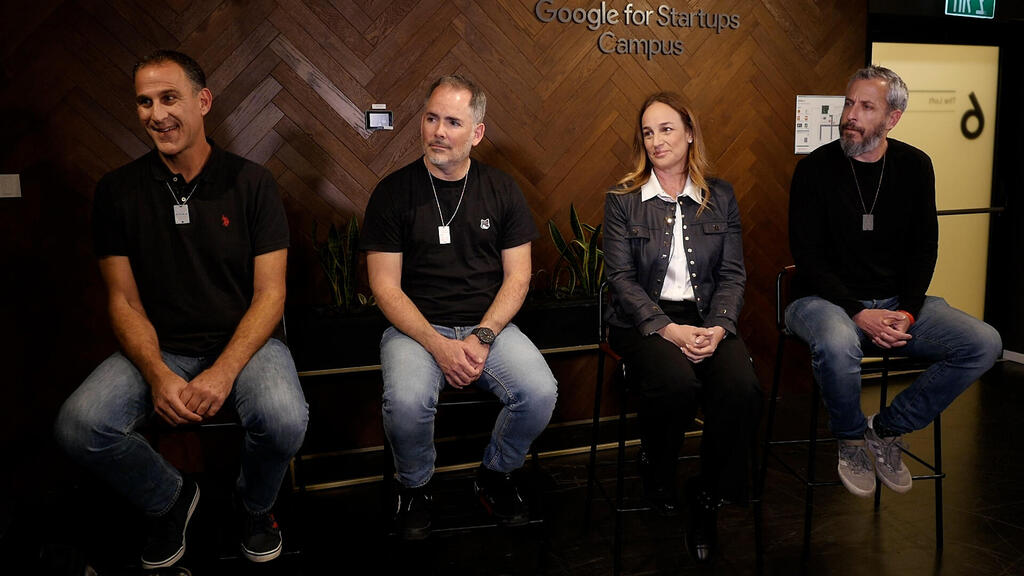


Startup Week panelists (from left) Barak Regev, Micah Kaufman, Dana Maor, Yonatan Edelsheim
(Photo: Sinai David)
Is AI disrupting the freelancer market? Are there any redundant jobs?
"In the United States, freelancers constitute approximately 50% of the labor market, rendering the distinction between them and full-time employees meaningless," said Micha Kaufman, co-founder and CEO of Fiverr. "While some jobs have become redundant, what sets this revolution apart is its speed. It's an acceleration phase of a sequence that began 150 years ago - the industrial revolution, automation, and the assembly line - tasks that render humans redundant in repetitive, non-emotional, non-creative roles. Even with tools like ChatGPT, which can produce confident-sounding but completely fabricated statements, supervision remains essential. GenAI will create more jobs than it will eliminate. We see new professions being created faster than old ones disappear, providing an opportunity for job creation. However, those who resist transformation will be left behind."
How should organizations adapt to this new reality?
Jonathan Edelshaim, CEO of Natural Intelligence, commented: "We're witnessing changes in roles like coding. Developers can now automate tasks and produce more, enabling us to allocate resources differently. We've begun leveraging early adopters and utilizing these tools to enhance efficiency across various roles. Working with partners like Google, we're exploring adjustments and opportunities for innovation to reach new segments and target audiences that were previously challenging to engage with using manual tools."
Barak Regev, Country Director of Google Israel, cited the evolution of cloud technology over the past decade as an example. "Many anticipated a decrease in IT jobs with the advent of the cloud, yet the opposite occurred," he noted. "New roles like DevOps emerged. Israel's ecosystem stands out as a technological frontrunner, and while many companies initially approached AI cautiously, Gen AI propelled them to new heights."